Understanding the Psychological Effects of Chronic Work Stress Among Essential Workers: Prevention Strategies for 2025

The Impact of Chronic Work Stress on Mental Health
Chronic work stress is a pervasive issue that affects the mental well-being of many individuals, particularly essential workers who face unique challenges in their roles. It is crucial to understand how chronic stress manifests in the workplace and the various factors that contribute to its prevalence among essential workers. Stressors such as irregular hours, emotional demands, and high-stakes situations can lead to significant mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression.
Understanding Burnout Prevention
Conclusion: A Collective Responsibility
Preventing burnout among essential workers is a collective responsibility that requires the commitment of individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. By prioritizing mental health and implementing effective burnout prevention strategies, we can create a supportive environment where essential workers can thrive. It is vital to recognize the ongoing challenges they face and to provide them with the necessary resources and support to sustain their well-being. Only through collaborative efforts can we ensure that essential workers are empowered to continue their crucial roles in society.
Encouraging Work-Life Balance
Achieving a healthy work-life balance is essential for preventing burnout, particularly for essential workers who often face unpredictable schedules. Organizations can support their employees by offering flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or adjusted hours. Additionally, promoting the importance of disconnecting from work outside of office hours can help employees recharge and reduce stress. Encouraging employees to take their vacation time and participate in leisure activities can further enhance their overall well-being.
The Role of Leadership in Burnout Prevention
Leadership plays a critical role in shaping workplace culture and influencing employees’ mental health. Effective leaders can model healthy behaviors, promote open communication, and prioritize employee well-being as part of the organizational mission. For example, leaders can encourage regular breaks, promote a culture of feedback, and demonstrate empathy towards employees’ challenges. By fostering a culture that values mental health, leaders can significantly reduce the risk of burnout among essential workers.
Implementing Effective Burnout Prevention Strategies
To effectively prevent burnout among essential workers, organizations must adopt a multi-faceted approach. This can include training managers to recognize signs of burnout, creating peer support groups, and ensuring that employees have access to mental health resources. For instance, implementing a buddy system can encourage employees to support one another and foster a sense of community in the workplace. Additionally, offering workshops on resilience-building can empower workers with tools to cope with stress more effectively.
Burnout prevention is not merely a personal responsibility but a collective effort that involves organizational policies, cultural shifts, and individual strategies. Organizations must recognize the signs of burnout and implement measures that promote a healthy work-life balance. This includes creating an environment where employees feel valued and supported. For instance, regular check-ins between managers and staff can foster open communication about workloads and stress levels.
Burnout prevention is essential to maintaining the mental health of essential workers and ensuring they can provide the necessary services effectively. This initiative encompasses various strategies, including self-care practices, organizational support systems, and community resources. By implementing proactive measures, both individuals and organizations can work towards preventing burnout and promoting resilience in high-stress environments. For example, mindfulness training and stress-reduction workshops can be beneficial for employees to manage stress more effectively.
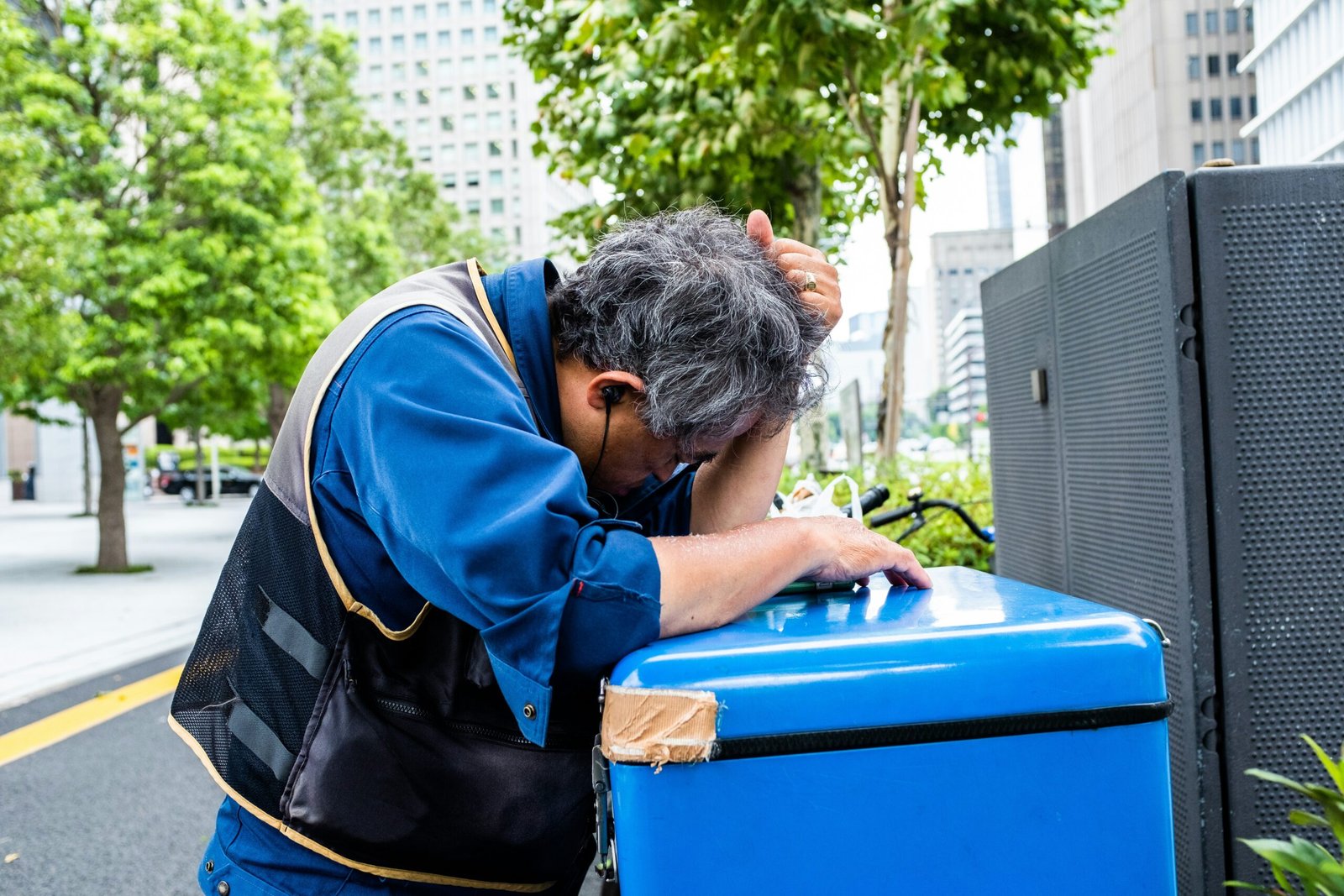
Chronic work stress has emerged as a significant concern for essential workers, profoundly influencing their mental health and complicating burnout prevention. Prolonged exposure to workplace stressors—such as high demands, tight deadlines, and inadequate support—can lead to a spectrum of mental health issues, notably anxiety, depression, and emotional exhaustion. Essential workers, who provide vital services across various sectors, often bear the brunt of these stressors, especially during unprecedented times, such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Additionally, the stigma surrounding mental health can prevent workers from seeking help, exacerbating their stress and leading to burnout.
Research indicates that approximately 42% of essential workers report symptoms of anxiety and depression, a stark increase compared to their non-essential counterparts. This elevated stress response can be attributed to various factors. The high-pressure environments in which they operate often necessitate quick decision-making and emotional resilience, contributing to feelings of overwhelm and fatigue. For instance, healthcare professionals, transit workers, and retail employees frequently face interactions with the public that can be stressful and unpredictable, which heightens their psychological burden. Furthermore, the ongoing effects of recent crises continue to impact their mental health, making it crucial for organizations to recognize these challenges.
Moreover, essential workers frequently encounter unique stressors during crises, such as natural disasters or public health emergencies. In such situations, the demand for their services surges, while their resources may remain limited. This disparity generates an environment ripe for chronic stress, leading to diminished mental well-being. The repercussions extend beyond the individual; worker mental health issues can adversely affect workplace productivity and organizational health. Burnout among employees can result in increased absenteeism, decreased morale, and higher turnover rates, creating a cycle that further perpetuates stress within the workplace. Organizations need to acknowledge these repercussions and act accordingly to support their workers.
In light of these challenges, it becomes increasingly crucial to address the mental health needs of essential workers and to integrate burnout prevention strategies. Fostering a supportive work environment, providing mental health resources, and implementing effective stress management strategies are vital to mitigating the psychological impacts of chronic work stress. Prioritizing mental health is not only beneficial for the individual but also for the organizations that rely on these dedicated workers. By offering counseling services, flexible work arrangements, and wellness programs, organizations can help reduce the incidence of burnout and enhance overall employee satisfaction and productivity.